The primary node in a GSM network is the MSC. It is the node, which controls calls both to MS’s and from MS’s. The primary functions of an MSC include the following:
• Switching and call routing:
A MSC controls call set-up, supervision and release and may interact with other nodes to successfully establish a call. This includes routing of calls from MS’s to other networks such as a PSTN.
• Charging:
An MSC contains functions for charging mobile calls and information about the particular charge rates to apply to a call at any given time or for a given destination. During a call it records this information and stores it after the call, e.g. for output to a billing center.
• Service provisioning:
Supplementary services are provided and managed by a MSC. In addition, the SMS service is handled by MSC’s.
• Communication with HLR:
The primary occasion on which an MSC and HLR communicate is during the set-up of a call to an MS, when the HLR requests some routing information from the MSC1.
• Communication with the VLR:
Associated with each MSC is a VLR, with which it communicates for subscription information, especially during call set-up and release.
• Communication with other MSC’s:
It may be necessary for two MSC’s to communicate with each other during call setup or handovers between cells belonging to different MSC’s.
• Control of connected BSC’s:
As the BSS acts as the interface between the MS’s and the SS, the MSC has the function of controlling the primary BSS node: the BSC. Each MSC may control many BSC’s, depending on the volume of traffic in a particular MSC service area. An MSC may communicate with its BSC’s during, for example, call set-up and handovers between two BSC’s.
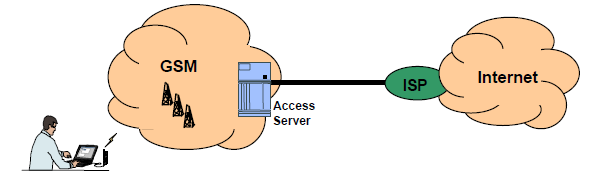
• Direct access to Internet services:
Traditionally, an MSC accessed the Internet nodes of an Internet Service Provider (ISP) via existing networks such as the PSTN. However, this function enables an MSC to communicate directly with Internet nodes, thus reducing call set-up time. Direct access can be provided by using an access server called Tigris (from Advanced Computer Communications). This may be integrated in an MSC or stand-alone connected to an MSC.
Internet access via GSM/PSTN (traditional method)
Direct access to Internet
• ISDN Primary Rate Access (PRA):
This function enables an MSC to provide PRA services to subscribers. One network operator can offer PABX connection services, through the PLMN. In this way the operator can compete directly with PSTN operators for ISDN business subscribers.

thnks
ReplyDelete:-d
ReplyDelete[-(
ReplyDeleteThanks☺️
ReplyDelete